In an age where bigger, better and faster seem to be best for everyone, manufacturers are always working to stay ahead of the game. Enter: the cloud, and the manufacturing industry may have found a game changer.
Let’s start with the basics and see just how it’s affecting our industry.
What you may know about the Cloud
The cloud is no more than a metaphor for the internet. Cloud computing involves the storing and/or processing of data or programs through the internet instead of through local (on-site) drives or networks. The distinction is that data and programs can be accessed via the internet anytime and anywhere.
What you may not know
The cloud is generally categorized as public or private. The public cloud operates via shared hardware owned by a third party. A private cloud is dedicated to one business. There are also hybrid clouds that combine features of both; most cloud services fall into the hybrid category.
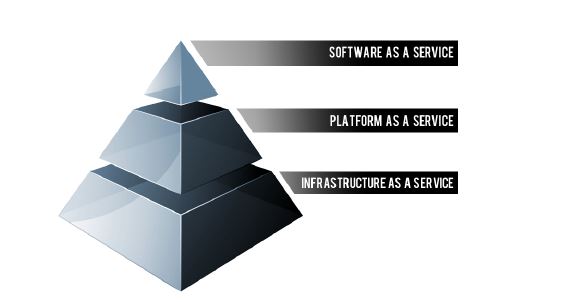
Often referred to as the “cloud computing stack,” there are three different categories of cloud service offerings for businesses, which increase in complexity as you move down the list:
- SaaS (Software-as-a-Service): a service providing applications over the internet
- PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service): a service providing an application platform over the internet
- IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service): a service providing computing infrastructure over the internet
SaaS is the most basic cloud service available. Salesforce, one of the best-known cloud service providers, describes their SaaS offering as a way to eliminate complex software and hardware management. There is no software to maintain or install—the provider manages the accessibility, performance, security, etc.—and the service can be customized. SaaS offerings would be sufficient for uses like online banking and email.
PaaS is the next step in cloud service. PaaS allows the user to create custom-built software applications with as many or as few tools as needed from the provider. The main idea is that PaaS reduces the custom-build process from a complex, expensive, and time-consuming endeavor (customized hardware and software, configuration, testing) to a log-in-and-get-started platform. PaaS might be a good fit when data is available, but where a new data management application needs to be designed and tested.
When a customizable application or a platform for creating your own application is not enough, there’s IaaS. IaaS providers host storage, hardware, software, servers, operating systems, and virtually all other components of infrastructure via the internet. IaaS makes the most sense where volatility is high; trial, temporary, or startup bases would be most likely to benefit from an IaaS subscription.
The Cloud Benefits for Manufacturing
It might be easy to envision the basic cloud benefits for personal use or even the technology and banking industries, but there are endless benefits for manufacturing as well. There is an enormous opportunity for improved efficiency and cost savings with cloud service offerings.
IT Savings
In the past, companies had to invest a ton of time and money with new project testing and launches. New hardware and software needed to be purchased to handle the anticipated project, and often those products depreciated or became obsolete before the new project was able to launch. Or worse, if the project failed, the company was left holding unusable IT products. Combine product costs with the man-hours needed to set up said technology, and it is easy to see why upgrades and advancements were slow moving and why new products are expensive for consumers.
Cloud services can be a solid solution when companies want to test a new product or idea because of customizable pay-as-you-need cloud features. If the testing goes well, cloud applications can be launched more quickly than with in-house technology, and all end-users will have simultaneous access thanks to the internet. If testing doesn’t go well, then the project can be scrapped without the deep losses associated with in-house hardware, software and labor costs.
Process Efficiency
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is particularly useful when combined with cloud services. ERP software is process management software that collects, stores, manages and interprets business data. With legacy ERP systems, some information isn’t available in real time. The delayed data reporting limits system and product control and can contribute to profit losses.
While ERP systems have been a huge benefit to the manufacturing sector, cloud ERP options like IQMS provide true real-time mobile business and operations monitoring. This instant accessibility enables immediate changes to improve operations with simultaneous updates to all users so that everyone in the business is on the same page at the same time.
Flexibility
One of the greatest manufacturing benefits of the cloud is the flexibility that the cloud services provide. In addition to IT and process flexibility, cloud services enable manufacturers to scale their business relative to demand. The real-time monitoring that ERP systems provide allows business owners or executives to see when product demands are fluctuating. Production can be adjusted instantly from a mobile device when added to an automated system. Because you can pay for features on a per-use or as-needed basis, you can add or remove features as often as you’d like to ensure that you are never paying for services that you don’t need.
Experts seem to agree that while there aren’t exact figures because of all the factors to be considered (IT salaries, storage needs, hardware and software, upgrades, etc.), the cloud seems to have excellent potential for the manufacturing industry.
How has the cloud affected your process or organization? Chat with us on Twitter @AppleRubber.