Urethane is an extremely versatile elastomer that is applied particularly where highly stressed parts are subject to wear. Engineers and manufacturers regularly rely on a variety of urethane parts, ranging from the smallest bushings, bearings and O-Rings to the materials used in agriculture, hydraulics, construction and other industries that our health, safety and well-being depend upon every day.
Let’s take a look at the different types, applications and limitations of urethane.
What is urethane?
Urethane compounds possess a combination of properties not available in any other thermoplastic material — they’re known for versatility, durometer, great resistance and tensile strength. Urethane combines some of the best properties of rubber and plastic without the weaknesses present in alternate materials. Urethane is easy to work with and is readily modified to suit a particular application through the addition of fillers, colors, stabilizers and lubricants.
There are two types of urethane rubber:
Polyester: Polyester urethanes have better oil and chemical resistance and can withstand high temperatures and heat aging.
Polyether: Polyether urethanes have great low-temperature flexibility, excellent abrasion and tear resistance as well as hydrolytic stability.

How are urethane seals produced?
Urethane is produced one of three ways. Let’s take a look at each:
1. Cast urethane
Cast urethane can be used to makes parts from a liquid process that is poured or injected into a mold to create parts. It can also be used to create rod stock to allow seal manufactures the ability to lathe cut different profiles. Cast parts can be multiple cavity tool allowing for multiple cycles and high volume output. Lastly, cut cast urethane can be used for one emergency replacement to large production runs. Our ExpresSeal® uses casted rod stock to produce high quality urethane parts.
Using ExpresSeal® technology, this method produces strong preproduction parts and allows companies to be the first to market and sell them. From prototypes to custom designs, ExpresSeal® is set up to respond quickly to the most challenging sealing requirements. The process is utilized to create seals used in construction, transportation, marine equipment, industrial production and other industries. Cast urethane performs better than other O-Ring elastomers in abrasion resistance and tensile strength. It surpasses the performance of millable urethane due to its higher tensile strength.
ExpresSeal® technology offers a variety of hydraulic and pneumatic seals in different profiles and offers fast prototyping and turnaround time.
Applications: Hydraulic pressure seals, wheels, rolls, slurry parts, bumpers, couplers, shock absorbers and wiper seals (for axially moving piston rods) are excellent applications. The cast rod process allows manufacturers to cut urethane into many different profiles to provide parts such as U-cups, O-Rings, V-shaped seals and other configurations.
Limitations: Cast polyurethanes are not recommended for exposure to concentrated acids and bases, ketones, esters, strong oxidizing agents, pure aromatic compounds and brake fluids. They are also not recommended for exposure to hot water or steam. Cast urethane durometers range from Shore A 70-90.

2. Millable urethane
Transfer and compression molding techniques produce parts made from millable urethane, which allows custom manufacturers to use the material in high-performance markets without purchasing expensive casting equipment. Millable urethane rubbers are solid polymers that can be processed on internal mixers and rubber mills. They can also be used to make excellent low-durometer roll coverings.
Engineers use traditional rubber molding equipment for millable urethane compounds. Sulfur or peroxide-cured compounds offer reduced compression set after the mold is cured. Millable polyester urethane possesses chemical compatibility similar to that of nitrile; it offers great resistance to petroleum-based oils, hydrocarbon fuels and hydraulic fluids, oxidizing effects of ozone and the aging effects of sunlight.
“Millable polyurethane is the polymer of choice for demanding applications requiring superior abrasion resistance and mechanical strength as well as oil and ozone resistance,” notes TSE, the world’s largest manufacturer of millable urethane rubber, sold under the tradename Millathane®.
Applications: Due to its impressive physical properties, properly designed compounds give superior explosive decompression resistance for down-hole applications in oil and gas. This can also be seen in carbon dioxide energized pellet guns, since the rapid release of the carbon dioxide does not cause blistering in the material.
Limitations: At elevated temperatures, millable urethane begins to soften, losing its physical strength and chemical resistance advantages over other polymers. When exposed to ketones, esters and concentrated acids, millable urethane can rapidly deteriorate.
3. Injection molded urethane
The process of injection molding forms thermoplastic urethane (or TPU) — high-tech material with a unique combination of useful properties. TPU is a thermoplastic elastomer that combines the mechanical and physical properties of rubber with the advantages of thermoplasticity and processability. TPU displays strong wear resistance to oils, greases and solvents as well as excellent weather stability and elasticity. Its unique characteristics make it extremely versatile material that outperforms many other thermoplastics.
TPU elastomers offers many benefits that plastic does not. With plastic, the higher the durometer, the more likely a part is to crack under impact. Urethane is not brittle like plastic; it is a true elastomer capable of tremendous impact resistance even at very high durometers. If plastic is stretched beyond a certain point, the material will remain permanently stretched. Urethane can be stretched to substantial elongations and will still return to its original dimensions. TPU closes the gap between rubber and hard thermoplastics.
“TPU is used successfully in numerous segments of the economy, such as the sports and recreation industry, industrial mechanical and automotive industry,” notes Bayer MaterialScience, a leading supplier of high-tech polymers. “Joining well-known applications such as transparent ski boots from leading manufacturers and center consoles inside vehicles produces new applications such as foldable kayaks, leg ropes for surfboards and breathable textiles.”
Applications: TPU can be molded for use in automobiles, caster wheels, food processing material handling equipment, in-line skates and medical tubing.
Limitations: TPU will deform as temperatures reach the melting point of a given polymer. Typical seal use is not recommended due to high compression-set values. Injection-molded TPU tends to be more expensive than other urethane options.
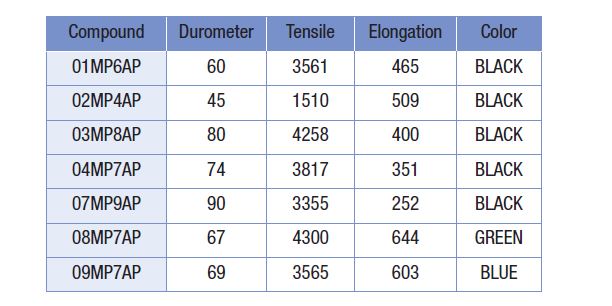
Urethane seals can be made from a variety of materials, depending on your application requirements. The following table highlights a few options:
Learn more about urethane
Our urethane processes offer a variety of hydraulic and pneumatic seals to meet your product development needs. For more benefits, sealing solutions or information on our urethane products, download our free ebook or contact our engineering team.
